Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM) Public-Private Partnerships for Conservation
Metolo Foyet_PhD Candidate (Tropical Conservation and Development) & Geography Instructor at UF Maxi Pia Louis_Director of NACSO
Fervently promoting active local involvement in natural resource management, CBNRM recognizes the importance of local participation, harnesses traditional knowledge, and aligns conservation efforts with community needs and aspirations, fostering a more sustainable an equitable approach. CBNRM has shown promising results and gained significance in promoting sustainable resource management due to several reasons:

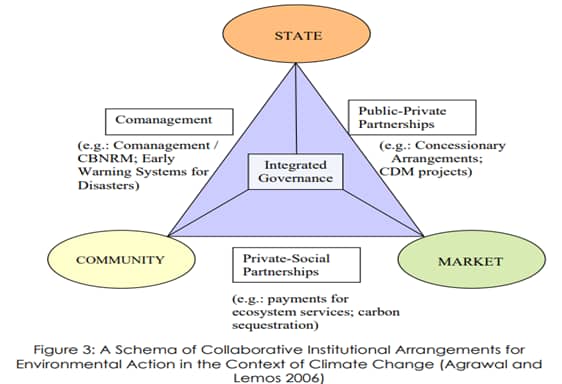
CBNRM Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
PPPs are collaborative arrangements between public sector entities (government agencies or local authorities) and private sector entities (businesses, NGOs, or community-based organizations) to address specific societal challenges or achieve common goals. In the context of CBNRM, PPPs can bring various benefits and contributions, such as (a) risk-sharing and long-term commitment, (b) increased funding, and (c) innovative solutions.
- (a) In PPPs, risks and responsibilities are shared among the partners. This ensures that the commitment to CBNRM is sustained, and the burden is not solely on the community or government.
- Shared interests of governments, businesses, and local communities in addressing climate change.
- (c) PPPs drive innovation, technology transfer, and market-driven solutions, while attracting private sector funding and resources to complement government budgets and community contributions towards supporting CBNRM projects and ensuring sustainability.
- PPPs for Climate Resilience and CBNRM: PPPs can facilitate the implementation of climate-resilient projects that incorporate CBNRM principles, blending private sector expertise and funding with government efforts for infrastructure and sustainable resource management practices. PPPs can be utilized to develop eco-tourism projects that conserve biodiversity and provide economic opportunities for local communities, prompting sustainable practices among businesses and climate goal alignment.
- CBNRM as a Factor in Climate Financing Decisions: When allocating climate financing, funders/investors often prioritize community involvement in projects, and initiatives emphasizing indigenous rights, social equity, and community support. CBNRM initiatives are seen as effective and sustainable, making them preferred options for climate funding.
Private and public partners can also:
- offer access to technical expertise and share knowledge for CBNRM initiatives, contributing insights on sustainable resource management practices, technology adoption, and efficient project implementation strategies.
- facilitate capacity building and training programs for local communities, equipping them with various skills in resource management, conservation, and sustainable livelihood.
- introduce innovative technologies (remote sensing, data analytics…) and approaches (coaching, transformational leadership…) for enhanced community-based management.
- establish market connections for community-produced goods and services, thus enhancing local livelihoods opportunities and making conservation more appealing, viable and sustainable.
- boost coordination and collaboration between various stakeholders (government, NGOs, private firms, and communities), thus fostering an integrated and holistic resource management and conservation strategy.
- Private sector partners can assist communities in policy advocacy and engagement with policy makers, leveraging their experience to promote favourable policies and regulations for sustainable resource management and community-driven conservation.
- Successful PPP models in CBNRM can be scaled up or replicated in various areas, resulting in wider-reaching benefits for biodiversity conservation and sustainable resource management.
For successful PPPs in CBNRM, it’s essential to prioritize the needs of local communities, emphasizing mutual trust, transparency, and respect for their rights and traditional wisdom. When designed thoughtfully, these partnerships can strongly support sustainable resource management, biodiversity conservation, and community empowerment.
Bridging for Biodiversity: CBNRM’s Climate-Smart Conservation Power
CBNRM yields various benefits for biodiversity conservation, ecosystem restoration, and climate change mitigation, including :
- CBNRM efforts like afforestation, reforestation, and sustainable forest management aid carbon sequestration, curbing greenhouse gas emissions for climate change mitigation.
- CBNRM encourages sustainable land use practices, curbing deforestation, soil degradation, and land-use change emissions, reducing the carbon footprint of local communities and supporting broader climate mitigation efforts.
- CBNRM’s emphasis on ecosystem and biodiversity protection indirectly aids climate change mitigation. Intact and healthy ecosystems function more efficiently in sequestering carbon and regulating climate patterns.
- With their in-depth knowledge of local ecosystems, communities adopt climate-resilient practices that enable them to adapt to changing climate conditions.
- CBNRM can stimulate community-led renewable energy ventures, like community-based solar or wind farms, diminishing fossil fuel dependency and fostering clean energy alternatives, thus decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- CBNRM programs can facilitate carbon offsetting schemes, where communities earn incentives for sequestering carbon through sustainable practices. Additionally, payment for ecosystem services (PES) models can reward communities for conserving forests or other carbon-rich ecosystems.
- Community-led advocacy and policy influence: CBNRM can empower local communities to engage in climate advocacy and policy discussions. By voicing their concerns and participating in decision-making processes, communities can influence policies that back climate change mitigation efforts.
- By engaging local communities, CBNRM can enhance environmental monitoring and reporting, including carbon emissions and sequestration rates. This data is valuable for assessing the effectiveness of climate change mitigation efforts.